

The digestive system is a vital part of the human body...

Liver disease can be caused by viruses, drugs, poisons, or...

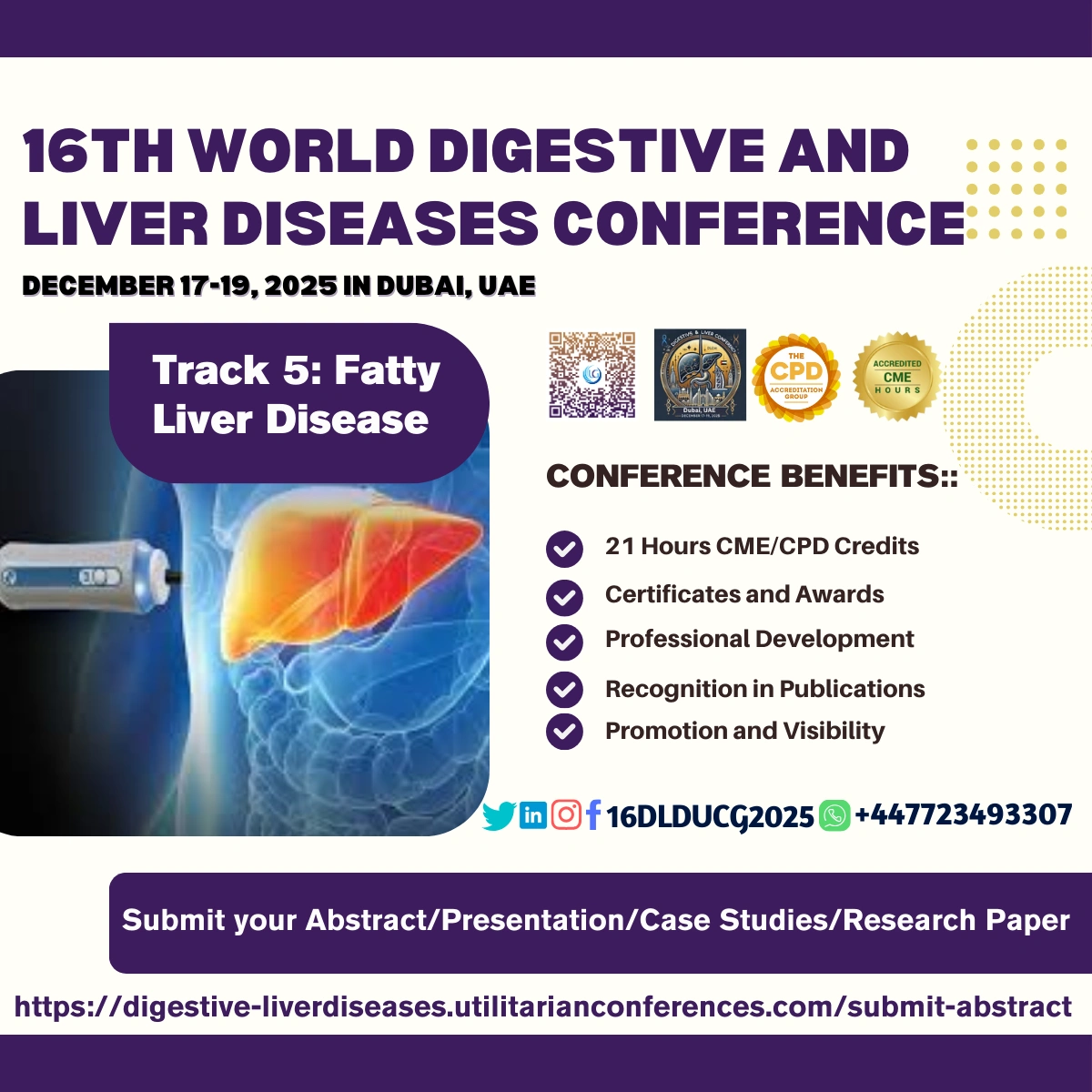
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic
steatosis, is a chronic condition where fat builds up in the
liver. It's common in Western countries, affecting about one in ten
people.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
Occurs in individuals who consume little to no
alcohol.
Often associated with obesity, diabetes, or
metabolic syndrome.
Includes two subtypes:
Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): Fat buildup in the
liver without inflammation or damage.
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Inflammation
and liver cell damage that can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver
cancer.
Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease:
Caused by excessive alcohol consumption, leading
to fat accumulation in the liver.
Can progress to alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or
liver failure if alcohol intake continues.
Symptoms Fatigue, Pain in the upper right
side of the abdomen, Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice),
Swelling of the legs or abdomen, and Confusion.
Causes obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2
diabetes, and insulin resistance.
Treatment
Lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and
weight loss
Medications to reduce cholesterol, triglycerides,
blood pressure, and diabetes
Limiting over-the-counter drugs
Complications
Inflammation of the liver, also known as
steatohepatitis
Cirrhosis, which can lead to liver failure and
cancer
Prognosis
Early-stage fatty liver disease usually doesn't
cause harm, but it can get worse
Many people with fatty liver disease have a normal
life expectancy
What is the diet for fatty liver
disease?
Aim for non starchy
vegetables and whole fruits. Choose leaner proteins like fish, poultry, beans,
and nuts. Limit red meats, cold cuts, bacon and other processed meats. Choose
whole grains like brown rice, oatmeal or whole wheat pasta.