

The digestive system is a vital part of the human body...

Liver disease can be caused by viruses, drugs, poisons, or...

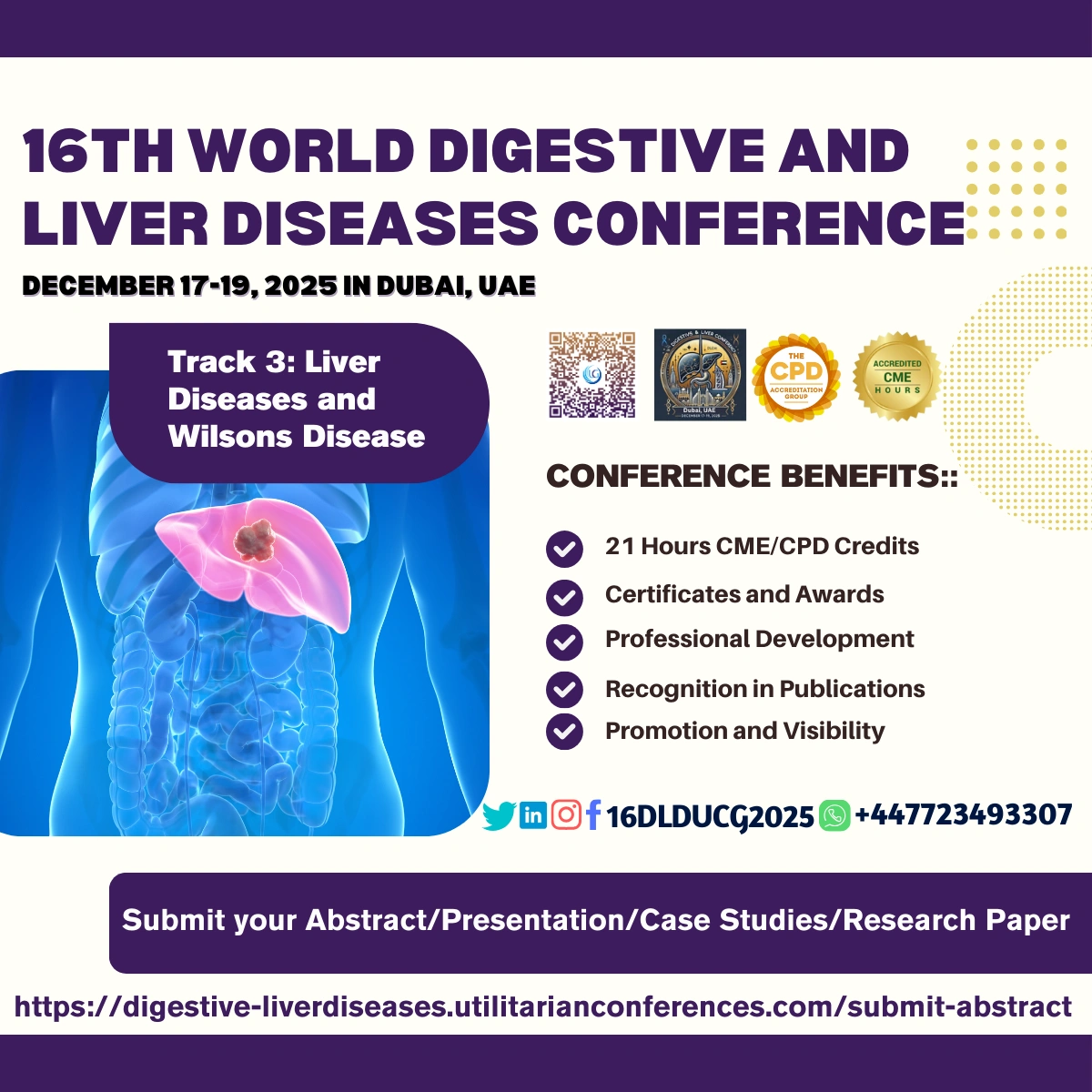
Liver Diseases Overview
Liver
diseases refer to any condition that affects the liver's structure or function.
The liver is crucial for filtering toxins, metabolizing nutrients, producing
bile, and storing vitamins. Common types of liver diseases include:
Hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E): Inflammation of the
liver caused by viral infections.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Fat accumulation in the
liver not related to alcohol.
Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases: Damage from excessive
alcohol intake, such as alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Autoimmune Liver Diseases: The immune system
attacks liver cells, e.g., autoimmune hepatitis.
Liver Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver
tissue due to long-term damage.
Liver Cancer: Includes hepatocellular carcinoma
and cholangiocarcinoma.
Genetic Liver Disorders: Conditions inherited
from parents, including Wilson’s disease.
Wilson’s Disease
Wilson’s disease is a rare genetic disorder in which
the body is unable to properly eliminate excess copper, causing it to
accumulate in the liver, brain, eyes, and other organs. It is an autosomal
recessive condition, meaning a person must inherit the defective gene from both
parents.
Causes
A
mutation in the ATP7B gene,
which regulates copper transport and excretion, leads to impaired copper
metabolism.
Excess
copper builds up in the liver initially and then leaks into the bloodstream,
affecting other organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms
vary depending on the organs affected and can be divided into categories:
Liver Symptoms:
Fatigue
Jaundice
(yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Hepatitis
(inflammation)
Liver
enlargement
Cirrhosis
(scarring of the liver)
Acute
liver failure in severe cases.
Neurological Symptoms:
Tremors
Difficulty
speaking or swallowing
Muscle
stiffness or lack of coordination
Behavioral
changes (depression, irritability).
Ophthalmological Symptoms:
Kayser-Fleischer Rings: Copper deposits in the
cornea, visible as brownish rings around the iris.
Other Symptoms:
Anemia
Low
platelet count
Kidney
issues or kidney stones
Arthritis.
Diagnosis
Blood Tests:
Low
levels of ceruloplasmin (a copper-carrying protein).
High
levels of free copper in the blood.
Urine Tests:
Elevated
copper excretion in a 24-hour urine sample.
Liver Biopsy:
Measurement
of copper levels in liver tissue.
Imaging:
Eye
examination for Kayser-Fleischer rings using slit-lamp microscopy.
Genetic Testing:
Identification
of mutations in the ATP7B gene.
Treatment
Medications:
Chelating Agents (e.g., Penicillamine,
Trientine): Bind to copper and help remove it through urine.
Zinc Acetate: Reduces copper absorption in the
intestine.
Dietary Restrictions:
Avoid
high-copper foods like shellfish, nuts, chocolate, and organ meats.
Liver Transplant:
Considered
for severe liver damage or acute liver failure.
Prognosis
With
early diagnosis and proper treatment, most patients lead healthy lives.
If
untreated, Wilson’s disease can result in severe liver damage, neurological
complications, or death.